Rohm claims the new microcontroller is the first to employ on-device AI learning without a network connection.
Rohm has debuted the industry’s first MCUs that can use solely on-chip AI to predict equipment anomalies in industrial edge-AI applications. These chips, the ML63Q253x-NNNxx/ML63Q255x-NNNxx (datasheet linked), are the first that can perform both AI learning and AI inference in the MCU without contacting an external AI server. The devices target predictive maintenance for industrial control and monitoring needs.
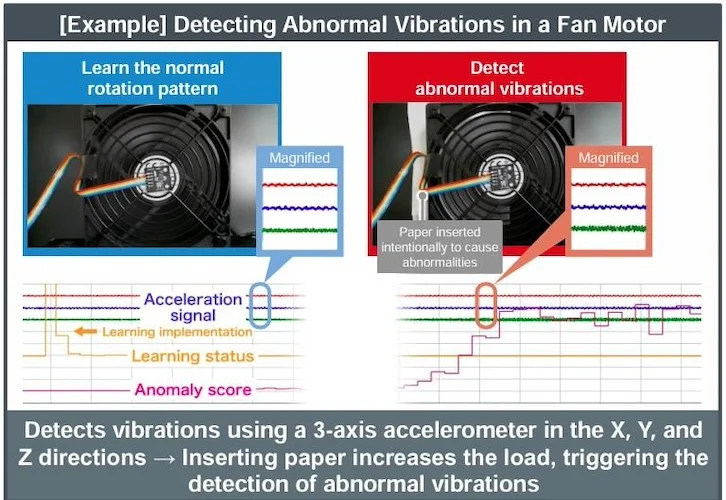
AI-based device characterization and AI-based failure prediction, all in the low-power, unconnected MCU.
The MCUs use self-contained AI to learn system behavior and detect early signs of failure. By eliminating the need for outside AI computational support, the MCUs reduce system development, implementation, and support costs.
Rohm Sets a New Precedent for AI MCUs
Rohm’s Solist-AI (Solution with On-device Learning IC for Standalone-AI) is the company's proprietary on-device AI solution. The system can perform both learning and inference on its own (a soloist) without relying on cloud or nearby servers. This capability delivers low power, remote operation without the overhead of wired or wireless network connections.
AI training and inference topology ranges from all-cloud-based computation to all-on-device computation, as is the case with Rohm's new MCUs. The highest cloud-weighted systems have the endpoint system only collecting data and acting on cloud-determined instructions, detailed in the “cloud-based AI” column below.

Variations of cloud-to-endpoint AI system topology.
Edge systems use cloud-based AI learning but offload the inference to a local server or workstation-class PC. The endpoint MCU still only passes data and executes instructions from the network (“edge AI” column). More recent MCUs have AI inference capability and only need the network to receive data tokens for the inference calculations or send data back to the cloud for inclusion in the AI model (“endpoint AI” column).
All of these topologies require a network connection to the cloud or a local high-performance CPU-based edge computer. Rohm’s AI MCUs perform both learning and inference in the MCU without external help.
AI Functionality Joins Suite of Advanced MCU Peripherals
The MCUs start with a 32-bit Arm Cortex M0+ at 48 MHz. From there, the chips add Rohm’s Solist-AI accelerator (AxlCORE-ODL) for AI learning and inference using a three-layer neural network. Variants are currently available in two packages: a 9 mm x 9 mm TQFP48 and a 12 mm x 12 mm TQFP64. Smaller 7 mm x 7 mm WQFN48 and 9 mm x 9 mm WQFN64 form-factor parts are in development.
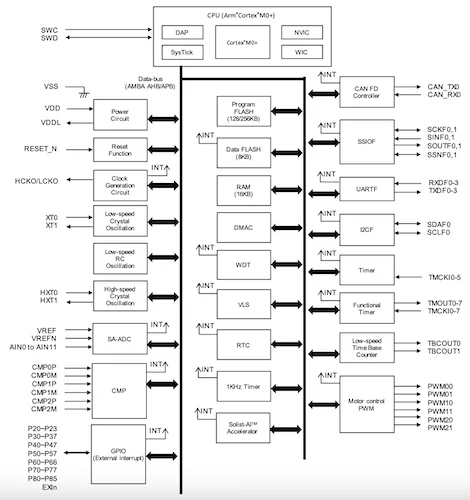
Block diagram of the ML63Q2500 series. See page 7 of the datasheet for an enlarged image.
In addition to the AI functionality, the chips are well-appointed with advanced MCU peripherals.
- Program memory: 128 or 256 Kbytes
- RAM data memory: 16 Kbytes
- Data flash memory: 8 Kbytes
- ISO 11898-1:2015-compliant CAN controller
- Multi-priority interrupt controller with one non-maskable interrupt source and 31 maskable interrupt sources
- Two-channel DMA controller
- Clocking system: Real-time clock, 1-kHz timer, time base counter, six-channel 16/32-bit timer, two 16-bit function timers, and watchdog timer
- Three-phase motor PWM
- Communications: Synchronous serial port (SSIOF), UART, I2C
- Up to 49 GPIO ports, eight being interrupt-capable
- Successive approximation type A/D converter, analog comparator, voltage-level supervisor
Developer Support
Rohm offers two development boards, one for the 48-pin ML63Q2537 and one for the 64-pin ML63Q2557. The company claims that an ecosystem partner will soon release an evaluation board for AI sensor effectiveness.
The chips and development boards are supported by Rohm’s LEXIDE-Ω integrated development environment. Lexide is an Eclipse-based environment familiar to most Arm developers. The Solist-AI Sim generates and evaluates AI models. Solist-AI Scope is a software scope for displaying the internal operation of the Solist-AI MCU in real-time.
Advancing Industrial AI by Breaking the Connection
While the MCU industry has been striving to create more connected devices, the new Rohm MCU series addresses the need for independent AI capability. Some AI applications require devices that can operate without “phoning home” for AI support. The Rohm ML63Q253x-NNNxx/ML63Q255x-NNNxx MCUs are the first to fully deliver on the endpoint AI promise.
All images used courtesy of Rohm Semiconductor.