Azure Cobalt 200 aims to deliver a 50% performance gain over its predecessor for real-world cloud workloads.
Microsoft has released the Azure Cobalt 200, its new Arm-based custom CPU. Engineered for cloud-native workloads and powered by the latest Arm Neoverse CSS V3 architecture, the new silicon is Microsoft’s latest step toward a more in-house silicon strategy.

Cobalt 200, Azure's newest cloud-native CPU. Image used courtesy of Microsoft
Azure Cobalt 200
Microsoft designed Cobalt 200 on Arm’s Neoverse CSS V3 platform and fabricated it using TSMC’s 3-nm process. The processor features 132 Arm Neoverse V3 cores per SoC, each with 3 MB of L2 cache, and a shared 192 MB of L3 system cache to support data-heavy compute operations.
The Cobalt 200 compute architecture is segmented across two chiplets connected via a custom high-bandwidth interconnect. Each chiplet integrates 66 CPU cores, totaling 132 cores per SoC. Accompanying the cores are six memory controllers supporting six DDR PHY memory channels, enabling high throughput and low-latency access. Custom memory controllers keep memory encryption always on by implementing Arm’s Confidential Compute Architecture (CCA) to isolate virtual machine memory from the hypervisor and host OS.
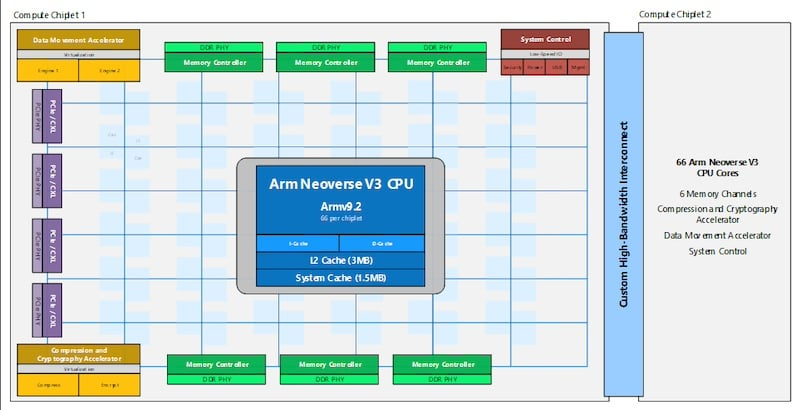
Cobalt 200 SoC block diagram. Image used courtesy of Microsoft
To support common compute patterns such as compression and encryption, Microsoft integrated dedicated accelerators directly into the silicon. These hardware blocks reduce CPU load by offloading compute-intensive tasks like data compression and cryptographic operations. According to internal benchmarks, offloading these functions improves workload efficiency, with Azure SQL benefiting from reduced core utilization.
For power efficiency, the architecture includes per-core Dynamic Voltage and Frequency Scaling (DVFS), which enables each core to operate independently and optimize power consumption in response to real-time workload demands.
The platform also incorporates Azure Boost, Microsoft’s networking and storage offload solution. Azure Boost improves network bandwidth and shifts remote storage tasks from the CPU to dedicated hardware, thereby improving I/O latency and overall performance. A built-in Azure integrated hardware security module (HSM) supports FIPS 140-3 Level 3 compliance and integrates with Azure Key Vault to provide scalable cryptographic key protection.
Inside the Neoverse CSS V3 Architecture
CSS V3 is Arm’s most advanced pre-integrated platform to date, purpose-built for high-performance, cloud-scale workloads. It supports the Armv9 instruction set and includes architectural enhancements such as Scalable Vector Extension 2 (SVE2) and CCA for secure memory isolation.
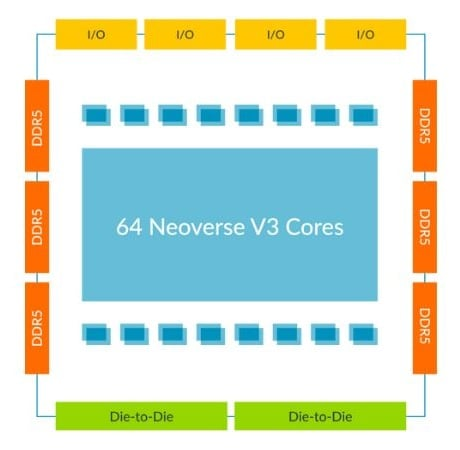
Per-die specifications of a Neoverse CSS V3 subsystem. Image used courtesy of Arm
Arm built CSS V3 to be modular, so that hyperscale cloud providers and silicon partners can focus on workload-specific optimizations without modifying the core design. To do this, Arm provides a verified subsystem with integrated fabric, cache coherence, and power management, reducing design complexity and time to silicon. CSS V3's approach also lets designers tune power and performance more granularly.
Moreover, CSS V3 includes built-in hooks for custom silicon extensions. It was this extensibility that allowed Microsoft to integrate unique features such as per-core DVFS and on-die accelerators without altering the core CPU logic.
Converged Compute at Scale
Where Cobalt 100 provided a strong foundation for cloud-native performance and energy efficiency, Cobalt 200 takes things further with custom accelerators, per-core power control, and tighter integration with Azure’s storage, security, and networking stacks. Cobalt 200-powered servers are currently operational in select Microsoft data centers, with general availability scheduled for 2026.