Infineon Levels Up Machine Learning Performance With Three New MCUs
Infineon has added three PSOC Edge MCUs with Arm Cores and dual-domain architectures to ramp up edge performance.
While the first microcontrollers (MCUs) were intended for system control and monitoring, modern MCUs are increasingly tasked with computing demands. With a growing push for connected devices to include machine learning (ML) at the edge, today’s MCUs must balance computing power and power efficiency at a small size and cost.
Infineon aims to strike this balance with its PSOC Edge E8 family of MCUs, which are optimized for performing machine learning at the edge.

The PSOC Edge E8 family.
PSOC Edge E8 Combines High Performance and Low Power
The PSOC Edge family includes the E81, E83, and E84 MCU series, each tailored for varying performance requirements and memory configurations for consumer and industrial applications. This portfolio stands out for its high-performance capabilities paired with low-power efficiency, critical for the always-on, responsive AI functionalities that modern IoT devices demand.
The PSOC Edge family can serve the high-performance domain for intensive ML tasks and a low-power domain for always-on ML functionalities. This is complemented by extensive peripheral support, on-chip memory, robust security features, and diverse connectivity options, including USB, CAN, Ethernet, Wi-Fi 6, and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE).
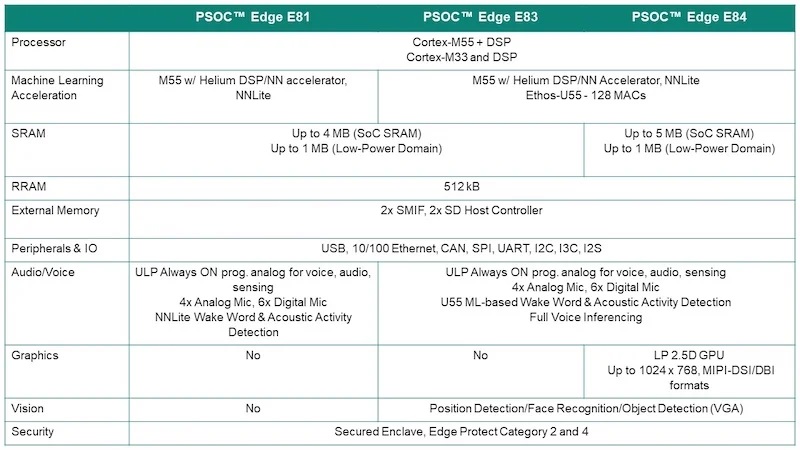
Spec comparison of the PSOC E81, E83, and E84 series.
The PSOC Edge E8x series' target applications span human-machine interfaces (HMI) in appliances and industrial devices to smart home systems, robotics, and wearables. Infineon designed the MCUs to facilitate a new level of interaction between users and devices, with voice/audio sensing for activation and control. The E83 and E84 also support vision-based interaction.
The series is backed by Infineon’s ModusToolbox software platform and the Imagimob Studio AI solution. These tools can help streamline the design process, allowing developers to quickly deploy machine learning models at the edge, a critical advantage in accelerating time to market for new products.
A Closer Look at the E81, E83, and E84
The E81 series focuses on advanced digital signal processing (DSP) and entry-level ML compute, integrating a 400-MHz Cortex-M55 and a Helium DSP alongside Infineon's NNLite Neural Network (NN) accelerator. This configuration is adept at handling tasks such as anomaly detection and acoustic event detection, which are becoming increasingly prevalent in edge devices.
The E81 series also offers up to 4 MB of SRAM for the system-on-chip (SoC), with an additional low-power domain of up to 1 MB, supporting efficient power management for always-on applications. Peripherals for this series include a 50.2 Msps 12-bit ADC, two 12-bit DACs, four integrated amplifiers, and four comparators.
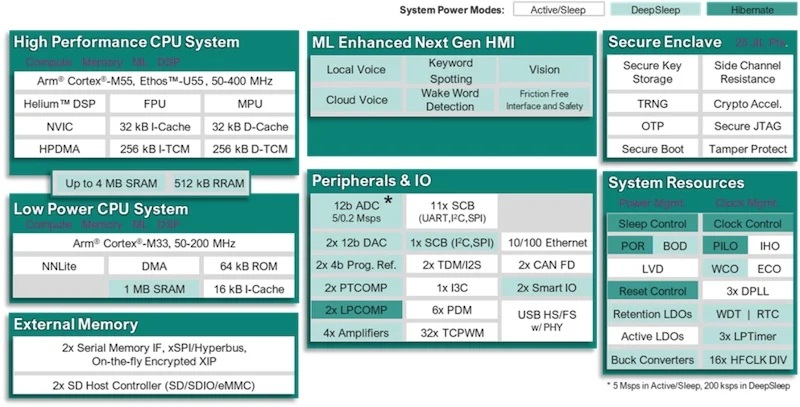
System block diagram of the E84 MCUs.
The E83 and E84 series step up the ML performance significantly by incorporating the Arm Ethos-U55 micro-NPU, which offers a 480-fold improvement over existing Cortex-M-based systems. This enables several HMI features, including advanced voice- and vision-based user interactions. The E84 series provides low-power graphics support for higher-resolution displays. The E84 also includes a low-power 2.5D graphics processing unit, supporting resolutions up to 1024 x 768. This enables it to render images and text for high-quality visual interfaces.
Improving Edge Computing
The PSOC Edge E8 family may help designers balance tradeoffs associated with modern edge computing by supporting both individual high-performance and low-power domains and leveraging the Helium DSP extension. Currently, the PSOC Edge E8 family is available for early-access customers only.



.jpg)